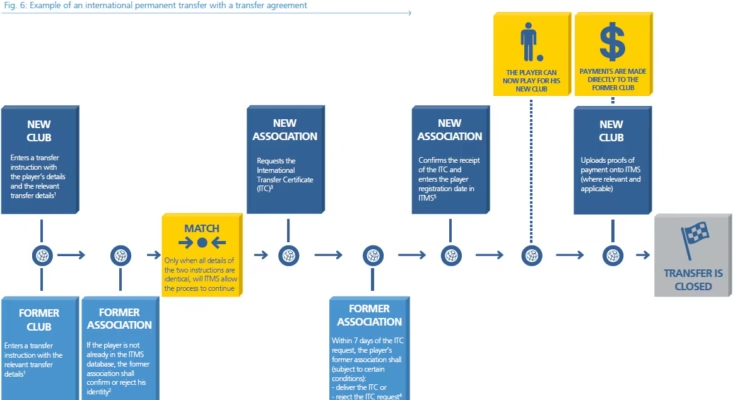
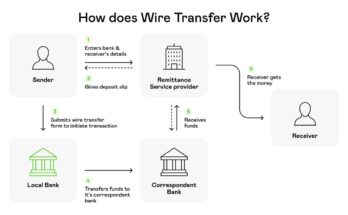
The United Kingdom’s legal system is built upon a complex framework of laws, regulations, and precedents that govern various aspects of society. One fundamental principle within this system is the concept of “transfer,” which pertains to the movement of rights, property, or obligations from one entity to another. Understanding the nuances of transfer laws in the UK is essential for both legal professionals and individuals engaged in activities involving the exchange of rights or property.
Types of Transfers in the UK Legal System
- Property Transfer: Property law in the UK allows for the transfer of ownership rights in both real and personal property. This process involves legal documentation, adherence to statutory requirements, and, in some cases, payment of taxes such as Stamp Duty Land Tax (SDLT). For instance, when transferring shares in a company, a stock transfer form must be completed and submitted to HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) for stamping. This form requires details of the shares being transferred, the consideration paid, and the identities of both the transferor and transferee. The stamped form is then used to update the company’s share register, finalizing the transfer of ownership. gov.uk
- Funds Transfer: In the financial sector, funds transfer regulations govern the movement of money between accounts, especially in the context of combating money laundering and terrorist financing. The Funds Transfer Regulation (FTR) mandates that payment service providers include accurate and full information about the payer and payee in electronic transfers. This information must accompany the transfer throughout the payment chain, ensuring transparency and traceability. Following the UK’s exit from the European Union, the FTR was incorporated into UK law, and institutions must comply with these requirements when processing payment transactions. ukfinance.org.uk
- Data Transfer: With the advent of digital technology, data transfer has become a critical area of concern. The UK adheres to data protection laws, primarily the Data Protection Act 2018, which governs the processing and transfer of personal data. These laws ensure that individuals’ personal information is handled securely and transparently, especially when transferred across borders. Organizations must obtain explicit consent from individuals before transferring their data and must implement adequate safeguards to protect the data during transit.
Legal Framework Governing Transfers
The UK’s legal framework for transfers is derived from a combination of statute law, common law principles, and European Union regulations that were retained post-Brexit. Key statutes include the Law of Property Act 1925, which outlines the procedures for transferring interests in land, and the Companies Act 2006, which governs the transfer of shares in companies. Additionally, the UK’s adherence to international conventions, such as the Hague Convention on the Law Applicable to Certain Rights in Respect of Securities Held with an Intermediary, influences the legalities surrounding cross-border securities transfers.
Challenges and Considerations
- Legal Formalities: Ensuring that all legal formalities are observed during a transfer is crucial. For property transfers, this includes proper execution of deeds, registration with relevant authorities, and payment of applicable taxes. Failure to adhere to these formalities can result in disputes over ownership and potential legal challenges.
- Regulatory Compliance: Transfers, especially in the financial sector, are subject to stringent regulatory oversight. Institutions must implement robust compliance programs to detect and prevent fraudulent activities, money laundering, and other financial crimes. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties and reputational harm.
- Cross-Border Issues: With globalization, many transfers involve international elements. Navigating the complexities of different legal systems, tax implications, and regulatory requirements requires careful planning and expert legal guidance.
Recent Developments
Post-Brexit, the UK has undertaken significant reforms to tailor its transfer laws to better suit its domestic interests while maintaining alignment with international standards. The incorporation of EU regulations into UK law has led to the creation of new statutes and amendments to existing laws, affecting how transfers are conducted. For example, the UK’s approach to data transfers has evolved to ensure that personal data continues to receive adequate protection, especially when transferred outside the UK.
Conclusion
The concept of transfer in the UK encompasses a broad spectrum of legal areas, each with its own set of rules and regulations. Whether dealing with property, funds, or data, understanding the legalities involved is essential to ensure that transfers are executed smoothly and in compliance with the law. As legal frameworks continue to evolve, staying informed about current laws and seeking expert legal advice when necessary will help navigate the complexities of transfers in the UK legal system.